Taxing The Country Into Welfare And Disability
“We contend that for a nation to try to tax itself into prosperity
is like a man standing in a bucket and trying to lift himself up by the handle.
It is impossible.”
Those were not the words of an Australian Commonwealth Treasurer but rather of Winston Churchill addressing the House of Commons in 1925 arguing against a proposed increase in taxes.

Almost 100 years after Churchill’s comment, Treasurer Chalmers presented his second Budget, in May 2023. It showed yet another record amount of tax collected and sums spent. For the coming 2024 financial year, the Government expects to collect $668 billion (25.9% of GDP) to fund $684 billion of spending (26.6% of GDP).
Of course, spending is higher than revenue so yet again
there is a deficit to add to the national debt pile
for our children and grandchildren to pay.
Of the $684 billion of spending, it is estimated that $356 billion or around 52% will be spent on health and welfare.

And within the social security and welfare line is the following:
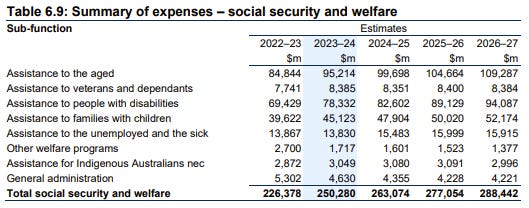
From a standing start around ten years ago, assistance to people with disabilities, ostensibly NDIS, is now the second largest Commonwealth government program.
Over the life of the budget (FY23 to FY27), the average annual increase in spending on the aged pension increases by 6.5%, but the average annual increase in spending on the NDIS is 7.9%. Both increases are faster than economic growth and the average annual increase in receipts (3.7%).

Like much of the developed world, Australia is experiencing an ageing population. It could be reasonably expected that spending on aged pensions might increase, but so much for superannuation.
Yet given the rapid growth of NDIS spending, one might conclude that
Australia is also experiencing a dramatic increase in disability.
Maybe there is something in the water. Or perhaps the education system.
Parked near the back of the budget papers is an analysis of real per-capita spending and taxing: per-capita to adjust for government activity increasing due to population increases; real to adjust for inflation over time. And in these numbers, the true state of budget disrepair is evident.
On a real per-capita basis, in the 2024 financial year:
- Commonwealth receipts are expected to be $18,102;
- Commonwealth payments are expected to be $18,479; and
- Commonwealth net debt is expected to be $15,574.
Impressive. From an average four-person household, the Commonwealth expects to extract $72,408.
But here is the interesting part. Thirty years ago, in per-capital real dollars:
- Commonwealth receipts were $8,866;
- Commonwealth payments were $10,110; and
- Commonwealth net debt was $11,364.
So basically, in the space of 30 years, on a per-capita basis, we are paying double the amount of tax, the Commonwealth is spending almost twice as much, and debt is 4.5 times larger in real terms. And 30 years ago was 1983-84, when Bob Hawke came in inheriting a national economic basket case.
It is worth noting that the inclusion of historical real per-capita data in the budget papers is owed to the negotiation efforts of former Senator David Leyonhjelm. Such important government finance transparency highlights the value of a strong classical liberal voice in Australian parliaments.

During the 1980 US Presidential election debate, Ronald Reagan asked the (rhetorical) question: “Are you better off than you were 4 years ago?” Here is a question for Australians. Is Australian government better than it was 30 years ago? Given the doubling of taxing and spending, are services better? Is Australia safer? Are we healthier or smarter?
Perhaps Churchill was only half right. A nation can’t tax itself into prosperity, but Australia is trying to tax itself into welfare and disability.







